Are you considering buying a new phone? Do the technical terms and specifications make you feel lost and overwhelmed? With so many options and features, it’s easy to get confused. Understanding phone specifications is essential to make an informed decision when purchasing a new phone. In this article, we will break down each specification, its function, and what makes it unique.
Understanding Phone Specifications: What Do They Mean?
Before we dive into the details of phone specifications, let’s first understand what they are. Phone specifications refer to the technical features and capabilities of a phone that determine its performance and functionality. These specifications help us understand how a phone works and what it can do.
Operating System
The OS of a phone is vital in understanding phone specifications. The operating system (OS) is the software that manages a phone’s hardware and software resources. There are two primary mobile operating systems: Android and iOS. Android is developed by Google and is used by many different phone manufacturers, while iOS is exclusive to Apple devices. The operating system determines the phone’s user interface, features, and app compatibility.
- Android: Android is an open-source operating system developed by Google. It is the most widely used operating system in the world and is used by many smartphone manufacturers, such as Samsung, Xiaomi, and OnePlus. Android is known for its flexibility, customization options, and wide range of apps available on the Google Play Store.
- iOS: iOS is a proprietary operating system developed by Apple and is used exclusively in iPhones. iOS is known for its user-friendly interface, security, and seamless integration with other Apple products and services. It also has a wide range of apps available on the Apple App Store.
- Windows: Windows is a proprietary operating system developed by Microsoft and is used in some smartphones, such as the Microsoft Lumia. Windows is known for its productivity features, such as Microsoft Office integration, and its ability to run desktop-like applications.
- BlackBerry: BlackBerry is a proprietary operating system developed by BlackBerry Limited and is used in some BlackBerry phones. BlackBerry is known for its security features, such as its encrypted messaging service, and its productivity features, such as BlackBerry Hub.
- KaiOS: KaiOS is a lightweight, web-based operating system developed by KaiOS Technologies Inc. KaiOS is designed to run on low-end phones and is used in phones such as the Nokia 8110 4G and the JioPhone. It provides basic smartphone features such as web browsing, social media apps, and messaging apps.
- HarmonyOS: HarmonyOS is an operating system developed by Huawei and is used in some Huawei phones. It is designed to work on a variety of devices, including smartphones, smart TVs, and wearables. HarmonyOS is known for its seamless device integration and its ability to provide a consistent user experience across devices.
Resolution
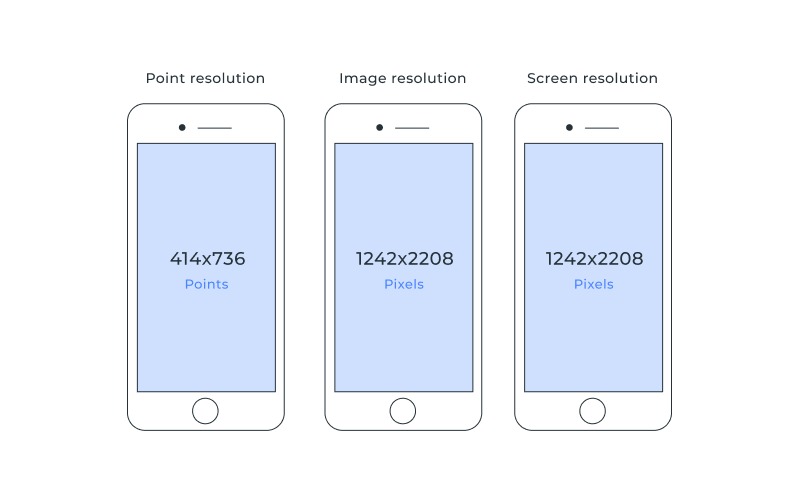
Resolution refers to the number of pixels displayed on the screen. The higher the resolution, the sharper and more detailed the image on your screen will appear. The reason why this is vital in understanding phone specifications is because most companies brag about the resolution of their brands. Phone displays usually have one of the following resolutions:
- HD (1280 x 720): HD is the minimum resolution for a modern smartphone display. HD displays have a pixel density of around 300 pixels per inch (ppi).
- Full HD (1920 x 1080): Full HD displays offer a higher pixel density of around 400 ppi, resulting in sharper and more detailed images.
- Quad HD (2560 x 1440): Quad HD displays have a pixel density of around 550 ppi and offer the sharpest and most detailed images on a smartphone.
See also: Samsung A53 Phone Review
See also: Tecno Phantom V Fold Review
Processor

The processor is the brain of the phone. It determines how fast the phone can process data and run apps. The two most common types of phone processors are Qualcomm Snapdragon and Apple A-series chips. Processors are measured in GHz (gigahertz) and the number of cores (e.g., dual-core, quad-core, octa-core). The higher the GHz and the more cores a processor has, the faster the phone will perform.
- Snapdragon: Snapdragon is a processor developed by Qualcomm, one of the leading semiconductor companies in the world. Snapdragon processors are known for their high performance and power efficiency. They are used in many Android phones, including Samsung, LG, and OnePlus.
- Exynos: Exynos is a processor developed by Samsung, one of the leading smartphone manufacturers in the world. Exynos processors are used in Samsung phones and are known for their high performance and power efficiency.
- A-Series: A-Series processors are developed by Apple and are used exclusively in iPhones. A-Series processors are known for their high performance and power efficiency. They are optimized to work seamlessly with Apple’s iOS operating system.
- Kirin: Kirin is a processor developed by Huawei, a leading smartphone manufacturer in China. Kirin processors are used in Huawei and Honor phones and are known for their high performance and power efficiency.
- MediaTek: MediaTek is a processor developed by MediaTek Inc., a Taiwanese semiconductor company. MediaTek processors are known for their affordability and are often used in mid-range and budget smartphones.
- Dimensity: Dimensity is a processor developed by MediaTek that is designed specifically for 5G smartphones. Dimensity processors are known for their high performance and power efficiency and are used in many 5G smartphones.
- Intel: Intel is a processor developed by Intel Corporation, one of the leading semiconductor companies in the world. Intel processors are mainly used in PCs, but they are also used in a few smartphones, such as the Asus Zenfone.
RAM
RAM (Random Access Memory) is where the phone stores temporary data when running apps. More RAM allows the phone to run multiple apps simultaneously and switch between them quickly. RAM is measured in GB (gigabytes), and the more RAM a phone has, the faster it will perform.
Storage/ROM
Storage refers to the amount of internal storage space a phone has for storing apps, photos, videos, and other files. Most phones offer storage capacities ranging from 32GB to 512GB. Some phones allow you to expand storage with a microSD card.
Display
The display is the screen on a phone. Display specifications include size, resolution, and type. The size of a phone’s display is measured diagonally in inches. The resolution refers to the number of pixels on the screen, and the higher the resolution, the sharper and more detailed the image. The type of display can be LCD or OLED, and each has its advantages and disadvantages. OLED displays offer better color accuracy and deeper blacks, while LCD displays are more affordable.
LCD (Liquid Crystal Display)
LCD displays are the most common type of display used in smartphones. They use liquid crystals to display images and have a backlight behind them. LCD displays can be further divided into two types:
- TFT LCD (Thin Film Transistor): TFT LCD displays are the most common type of LCD displays. They provide good color reproduction, wide viewing angles, and fast refresh rates.
- IPS LCD (In-Plane Switching): IPS LCD displays are an improved version of TFT LCD displays. They provide better color accuracy and wider viewing angles.
OLED (Organic Light Emitting Diode)
OLED displays use organic compounds to create light and do not require a backlight. This allows them to produce deep blacks and high contrast ratios. OLED displays can be further divided into two types:
- AMOLED (Active Matrix OLED): AMOLED displays use a thin-film transistor (TFT) backplane to control the flow of electricity to each pixel. This allows for faster refresh rates and better power efficiency.
- PMOLED (Passive Matrix OLED): PMOLED displays do not use a TFT backplane and are typically used in smaller displays, such as smartwatches. They are less power-efficient than AMOLED displays and have lower resolution.
Micro-LED
Micro-LED displays use tiny LED lights to create images and do not require a backlight. They provide high brightness levels, wide color gamut, and low power consumption. However, they are currently expensive to produce and are not widely available in smartphones yet.
E Ink
E Ink displays use electronic ink particles to display text and images. They are commonly used in e-readers and provide high contrast and low power consumption. However, they are not suitable for displaying video or animation.
Understanding the different types of displays can help you choose the right phone that meets your needs and preferences.
See also: What does AMOLED Display Mean?
See also: What does OLED Display Mean?
Battery

The battery is what powers a phone. Battery specifications include capacity (measured in mAh – milliamp-hours) and charging technology. The higher the battery capacity, the longer the phone can last between charges. Fast charging technology allows the battery to charge quickly, and some phones support wireless charging.
Camera

The camera is an essential feature for many smartphone users. Camera specifications include resolution, aperture, and lens type. The higher the resolution, the more detail the camera can capture. A wider aperture allows more light into the camera, resulting in better low-light performance. The lens type can be a standard lens, wide-angle lens, or telephoto lens, each offering unique benefits.
- Rear Camera: The rear camera is the primary camera on a phone, and usually has a higher megapixel count than the front camera. It’s used for taking photos and videos.
- Front Camera: The front camera is used for taking selfies and video calls. It usually has a lower megapixel count than the rear camera.
Connectivity
Connectivity specifications determine how your phone connects to the internet and other devices. The two most common types of connectivity are:
- Wi-Fi: Wi-Fi allows your phone to connect to wireless networks, so you can access the internet without using cellular data.
- Bluetooth: Bluetooth allows your phone to connect wirelessly to other Bluetooth-enabled devices, such as headphones, speakers, and other phones.
Biometrics
Biometric specifications refer to the phone’s ability to identify the user using unique biological characteristics, such as fingerprints or facial recognition. The two most common types of biometric authentication are:
- Fingerprint: Fingerprint authentication uses a sensor to scan the user’s fingerprint and match it to a stored template. This is a secure and convenient way to unlock your phone.
- Face recognition: Face recognition uses a front-facing camera to scan the user’s face and match it to a stored template. This is a convenient way to unlock your phone, but it may not be as secure as fingerprint authentication.
Audio
Audio specifications include the speaker and microphone quality. The speaker’s quality affects how clear and loud the phone’s sound is, while the microphone’s quality affects the phone’s call and recording quality. Some phones offer features such as stereo speakers or noise-cancellation technology.
Understanding Phone Specifications
Understanding phone specifications is crucial for making an informed decision when purchasing a new phone. Each specification plays a vital role in the phone’s performance and functionality. By understanding what each specification means and what makes it unique, you can choose the phone that best suits your needs and preferences.
FAQs
Q1: What is the difference between LCD and OLED displays?
OLED displays offer better color accuracy and deeper blacks, while LCD displays are more affordable.
Q2: How much RAM do I need for a phone?
It depends on your usage. If you use many apps simultaneously, you’ll need more RAM.
Q3: Can I expand a phone’s storage capacity?
Some phones allow you to expand storage with a microSD card.
Q4: What is the difference between a standard lens and a telephoto lens?
A standard lens captures images at a typical field of view, while a telephoto lens magnifies the subject, allowing for closer shots.
Q5: Does a higher battery capacity always mean a longer battery life?
Not necessarily. The battery life also depends on factors such as the phone’s display size and resolution, processor, and usage.




Add Comment