In recent years, OLED displays have become increasingly popular, especially in the field of consumer electronics. OLED technology has revolutionized the display industry, providing an unprecedented level of color accuracy, contrast, and black levels. However, what does OLED display mean? In this article, we will delve deep into the workings of OLED displays, exploring their features, benefits, and drawbacks.
Introduction: What Does OLED Display Mean?
Organic Light Emitting Diode (OLED) is a display technology that uses organic compounds to emit light when an electric current is applied. The OLED technology is used in various electronic devices, including smartphones, TVs, computer monitors, and smartwatches. The OLED displays have several advantages over traditional displays, such as LED and LCD, making them the preferred choice for many consumers.
What is OLED Technology?
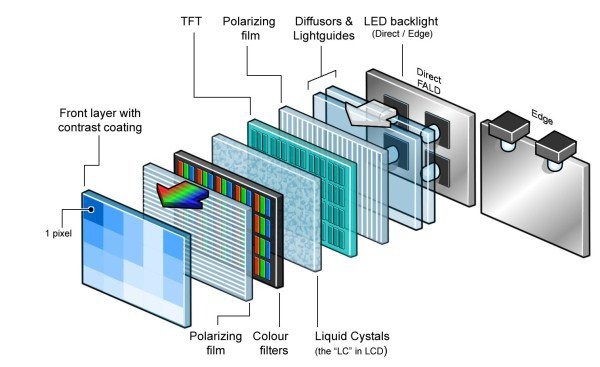
OLED Display Structure
An OLED display consists of several layers of organic materials sandwiched between two electrodes. The organic materials used in OLED displays are carbon-based and emit light when electricity is applied. The OLED display layers include:
- Substrate: It is the base layer of the OLED display, which provides mechanical support to the display.
- Anode: It is a transparent electrode made of indium-tin-oxide (ITO) that conducts electricity from the substrate to the organic layers.
- Hole Injection Layer (HIL): This layer helps in the efficient transfer of holes from the anode to the organic layers.
- Emissive Layer: This layer consists of organic compounds that emit light when electricity is applied.
- Electron Injection Layer (EIL): This layer helps in the efficient transfer of electrons from the cathode to the organic layers.
- Cathode: It is another transparent electrode made of ITO that conducts electricity from the organic layers to the substrate.
Working of OLED Display
When a voltage is applied to the OLED display, the anode injects holes into the emissive layer, while the cathode injects electrons. These injected holes and electrons recombine in the emissive layer, releasing energy in the form of light. The color of the emitted light depends on the organic materials used in the emissive layer. OLED displays can produce a wide range of colors, making them suitable for applications that require high color accuracy.
See also: What does AMOLED Display Mean?
Advantages of OLED Displays
OLED displays have several advantages over traditional displays, including:
- Better Contrast: OLED displays have a higher contrast ratio than LCD displays, providing deeper blacks and brighter whites.
- Wide Viewing Angles: OLED displays offer wider viewing angles than traditional displays, providing a better viewing experience.
- Faster Refresh Rate: OLED displays have a faster refresh rate than LCD displays, making them suitable for applications that require fast-moving images.
- Thinner and Lighter: OLED displays are thinner and lighter than traditional displays, making them ideal for portable devices.
Disadvantages of OLED Displays
Despite their advantages, OLED displays have some drawbacks, including:
- Burn-In: OLED displays are susceptible to burn-in, which occurs when static images remain on the screen for a prolonged period, causing permanent damage to the display.
- Limited Lifespan: OLED displays have a limited lifespan compared to traditional displays, especially when exposed to direct sunlight or high temperatures.
- Higher Cost: OLED displays are more expensive to manufacture than traditional displays, making them less accessible to some consumers.
Types of OLED Displays
There are several types of OLED displays available in the market, including:
1. Passive Matrix OLED (PMOLED)
PMOLED displays are made up of simple grids of pixels, making them suitable for applications that require basic displays, such as simple numeric displays.
2. Active Matrix OLED (AMOLED)
AMOLED displays have a more complex structure than PMOLED displays, consisting of a thin-film transistor (TFT) backplane that controls each pixel’s brightness independently. AMOLED displays offer higher resolution and color accuracy than PMOLED displays, making them suitable for advanced applications such as smartphones and TVs.
3. Transparent OLED (TOLED)
TOLED displays are transparent and can be used to create see-through displays, making them suitable for applications such as head-up displays (HUDs) and augmented reality (AR) glasses.
4. Top Emission OLED (TEOLED)
TEOLED displays emit light from the top layer of the display, allowing for more efficient light extraction and higher brightness.
5. Foldable OLED (FOLED)
FOLED displays can be bent or folded without damaging the display, making them suitable for foldable devices such as smartphones and tablets.
See also: Samsung A53 Phone Review
See also: Tecno Phantom V Fold Review
Applications of OLED Displays
OLED displays are used in a wide range of electronic devices, including:
- Smartphones and Tablets
- TVs and Monitors
- Smartwatches and Fitness Trackers
- Car Displays and HUDs
- Lighting and Signage
OLED vs. LCD Display Technology
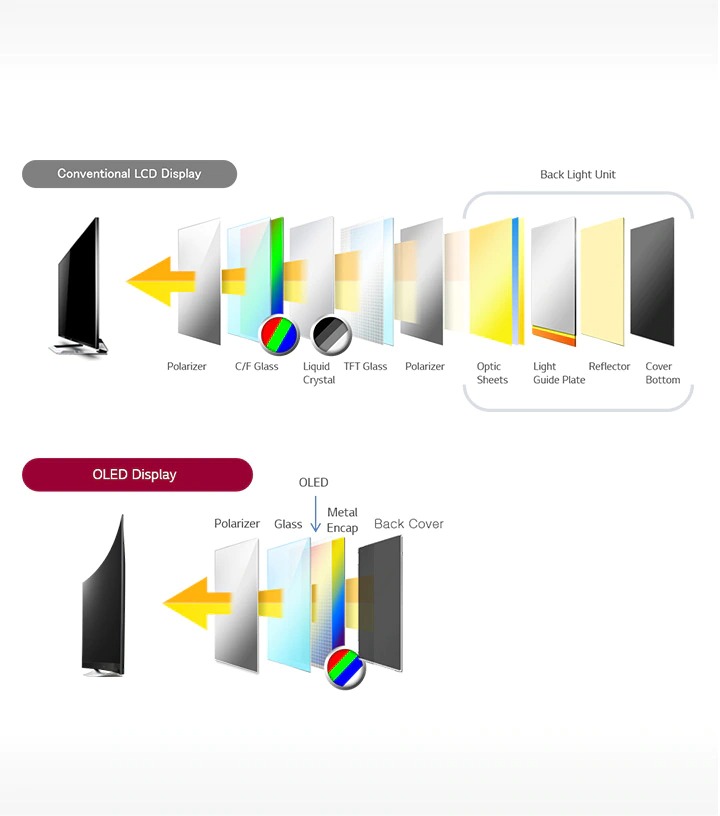
LCD displays use a backlight to illuminate the display, while OLED displays emit their light, resulting in better contrast and black levels. OLED displays also offer wider viewing angles, faster refresh rates, and thinner form factors than LCD displays.
OLED vs. LED Technology
LED displays are made up of small light-emitting diodes that produce light, while OLED displays use organic compounds to emit light. OLED displays offer better contrast and black levels than LED displays, making them suitable for applications that require high color accuracy.
OLED vs. QLED Technology
QLED displays use quantum dots to produce color, while OLED displays use organic compounds. OLED displays offer better contrast and black levels than QLED displays, but QLED displays offer better brightness and color accuracy.
OLED Display Market Overview
The global OLED display market is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 14.7% from 2021 to 2028, driven by the growing demand for OLED displays in smartphones, TVs, and other electronic devices.
Conclusion: What Does OLED Display Mean?
OLED displays are a revolutionary technology that offers several advantages over traditional displays. Despite their higher cost and limited lifespan, OLED displays are widely used in a wide range of electronic devices, including smartphones, TVs, and smartwatches. With the growing demand for high-quality displays, OLED technology is expected to continue its rapid growth in the coming years.
FAQs
1. What does OLED stand for?
OLED stands for Organic Light Emitting Diode.
2. What are the advantages of OLED displays?
OLED displays offer better contrast, wider viewing angles, faster refresh rates, and thinner form factors than traditional displays. They also offer higher color accuracy and better black levels.
3. What are the disadvantages of OLED displays?
OLED displays have a limited lifespan, are susceptible to burn-in, and are more expensive to manufacture than traditional displays.
4. What are some popular applications of OLED displays?
OLED displays are commonly used in smartphones, TVs, and smartwatches. They are also used in car displays, lighting, and signage.
5. What is the difference between OLED and LCD displays?
LCD displays use a backlight to illuminate the display, while OLED displays emit their light. OLED displays offer better contrast, black levels, and viewing angles than LCD displays.









Add Comment